
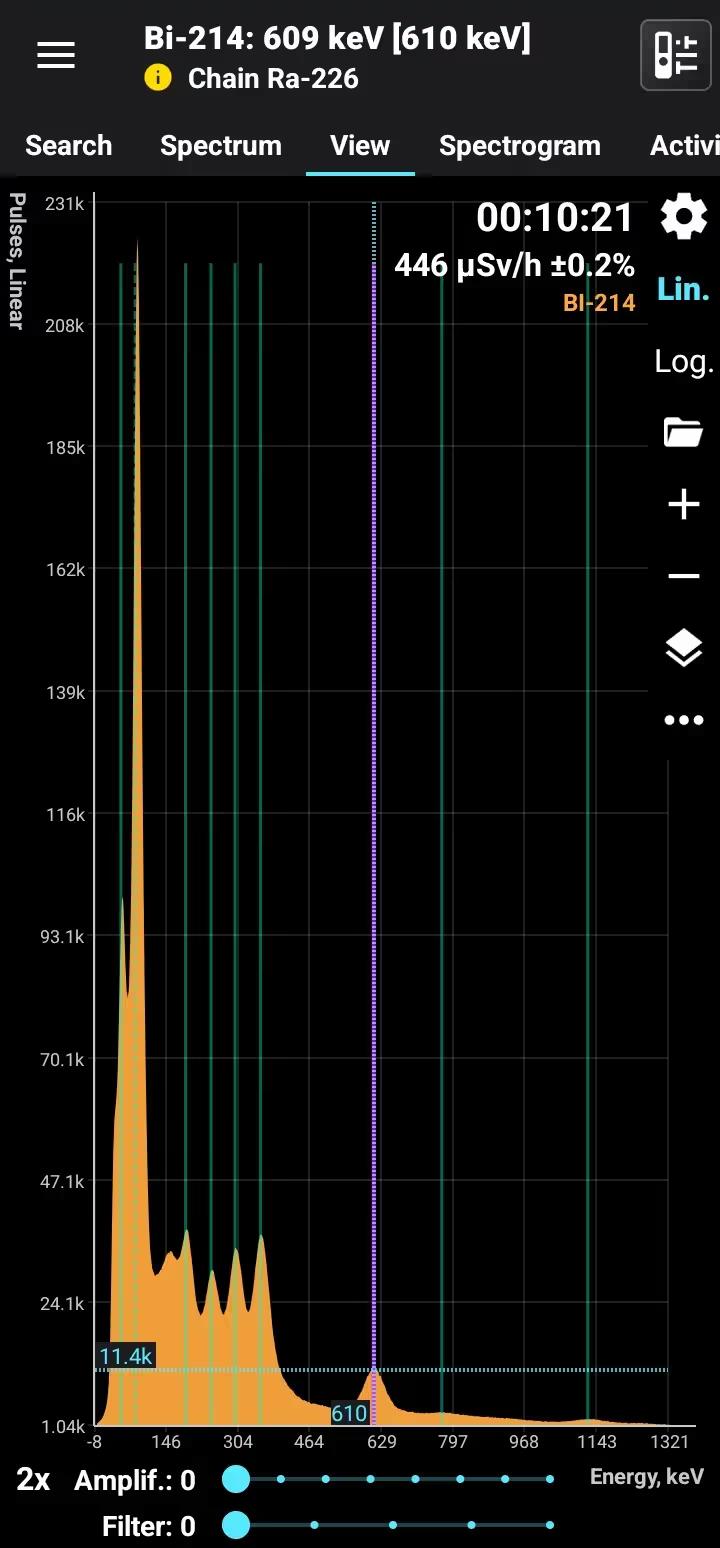
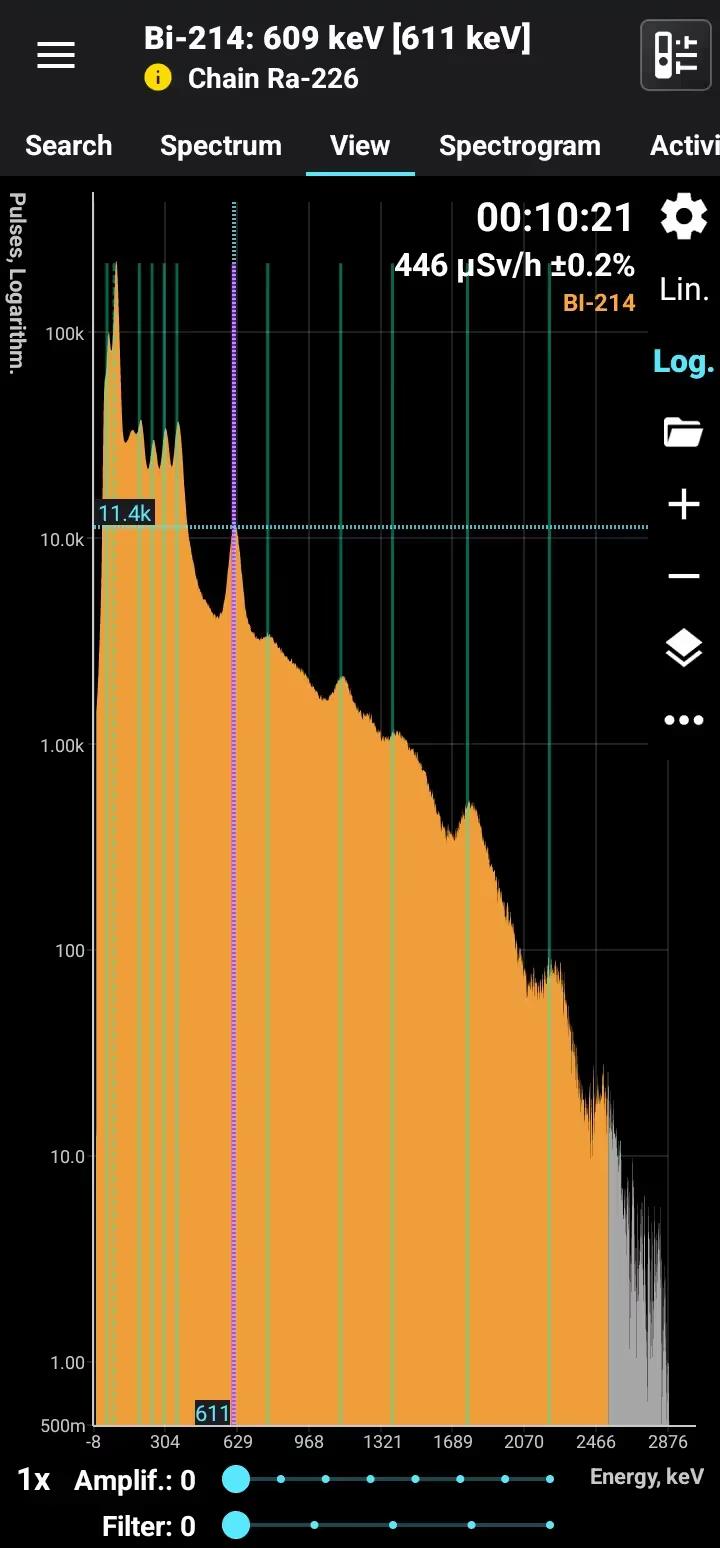
Bismuth-214 (Bi-214) is a radioactive isotope of bismuth with a half-life of approximately 19.9 minutes. It is part of the uranium-238 decay series, formed as a decay product of radon-222 through polonium-218 and lead-214. Bi-214 decays primarily via beta emission to polonium-214, accompanied by strong gamma radiation at characteristic energies, making it highly detectable using gamma spectrometry.
This isotope is almost always present in a mixture with other isotopes characteristic of the decay chain of uranium, radium or radon.

Bi-214 is widely used in environmental monitoring and radiation detection calibration due to its strong gamma emissions. In research, Bi-214 is studied to understand decay chains and natural radiation distribution. It also plays a role in validating radiation models and monitoring radon progeny in indoor air quality studies.

Bi-214 is naturally found as part of the uranium-238 decay chain and is present in trace amounts in environments with uranium-bearing minerals, such as uraninite and pitchblende. It is commonly encountered in soils, rocks, and groundwater in areas with high uranium content. Bi-214 is also found in the atmosphere as a decay product of radon-222, contributing to natural background radiation. Its strong gamma emissions make it a critical component in environmental radiation monitoring and uranium exploration.
Bi-214
Bismuth-214
Half-life: 19.9 min Main emission lines: 609, 1120, 1760 keV Decay chain: Ra-226 Related lines: 47, 78, 186, 242, 295, 351, 2200 keV
Decay mode Alpha
Alpha
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 5452 | 0.0113 |
| 5516 | 0.0082 |
| 5273 | 0.00122 |
| 5184 | 0.000128 |
Decay mode Beta-
Beta-
| Avg. En., keV | Intensity, % | Decay En., keV |
| 1268 | 19.2 | (3269) |
| 539 | 17.55 | (1539) |
| 525 | 16.90 | (1504) |
| 492 | 8.16 | (1422) |
| 683 | 7.22 | (1891) |
| 352 | 5.56 | (1065) |
| 385 | 4.33 | (1150) |
| 615 | 3.09 | (1726) |
| 261 | 2.78 | (821) |
| 424 | 2.459 | (1252) |
| 475 | 1.589 | (1379) |
| 427 | 1.433 | (1258) |
| 248 | 1.28 | (787) |
| 433 | 1.192 | (1274) |
| 668 | 0.90 | (1853) |
| 356 | 0.866 | (1076) |
| 567 | 0.57 | (1608) |
| 318 | 0.563 | (976) |
| 1007 | 0.55 | (2660) |
| 161 | 0.542 | (540) |
| 373 | 0.46 | (1121) |
| 165 | 0.273 | (550) |
| 173 | 0.249 | (574) |
| 350 | 0.22 | (1060) |
| 204 | 0.20 | (664) |
| 328 | 0.192 | (1003) |
Gamma
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 609.321 | 45.44 |
| 1764.491 | 15.29 |
| 1120.294 | 14.90 |
| 1238.122 | 5.83 |
| 2204.10 | 4.92 |
| 768.360 | 4.89 |
| 1377.669 | 3.985 |
| 934.056 | 3.094 |
| 1729.595 | 2.87 |
| 1407.988 | 2.388 |
| 1509.211 | 2.127 |
| 1847.433 | 2.027 |
| 1155.210 | 1.634 |
| 2447.69 | 1.545 |
| 665.446 | 1.540 |
| 1280.976 | 1.435 |
| 1401.515 | 1.333 |
| 806.179 | 1.262 |
| 2118.51 | 1.156 |
| 1661.274 | 1.046 |
| 1385.310 | 0.801 |
| 1583.203 | 0.708 |
| 703.10 | 0.482 |
X-rays
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 79.290 | 0.686 |
| 9.655 - 16.929 | 0.61 |
| 76.862 | 0.412 |
| 89.254 - 92.628 | 0.310 |
| 89.254 - 90.419 | 0.236 |
| 92.248 - 92.382 | 0.0735 |