
Americium-241 (Am-241) is a radioactive isotope of americium with a half-life of approximately 432.2 years. It primarily undergoes alpha decay, emitting alpha particles and low-energy gamma radiation. Am-241 is a byproduct of plutonium-241 decay, typically produced in nuclear reactors during the operation of nuclear fuel cycles. Its alpha decay is accompanied by gamma radiation, which makes it useful for a variety of applications.

Am-241 is widely used in industrial and scientific applications. One of its most common uses is in smoke detectors, where its alpha radiation ionizes air to detect smoke particles. It is also utilized as a gamma source for calibration of radiation detection equipment and in industrial gauges to measure thickness, density, and moisture. In scientific research, Am-241 serves as a source of alpha particles for experiments and as a component in neutron sources, where it is mixed with beryllium to produce neutrons.

Am-241 is not found naturally and is produced as a byproduct in nuclear reactors, specifically during the decay of plutonium-241 in spent nuclear fuel. It is encountered in controlled environments, such as research laboratories, industrial facilities, and in consumer devices like smoke detectors. Trace amounts of Am-241 may also be present in nuclear waste and areas affected by nuclear activities. Due to its long half-life and radiotoxicity, its use and disposal are strictly regulated to ensure safety and environmental protection.
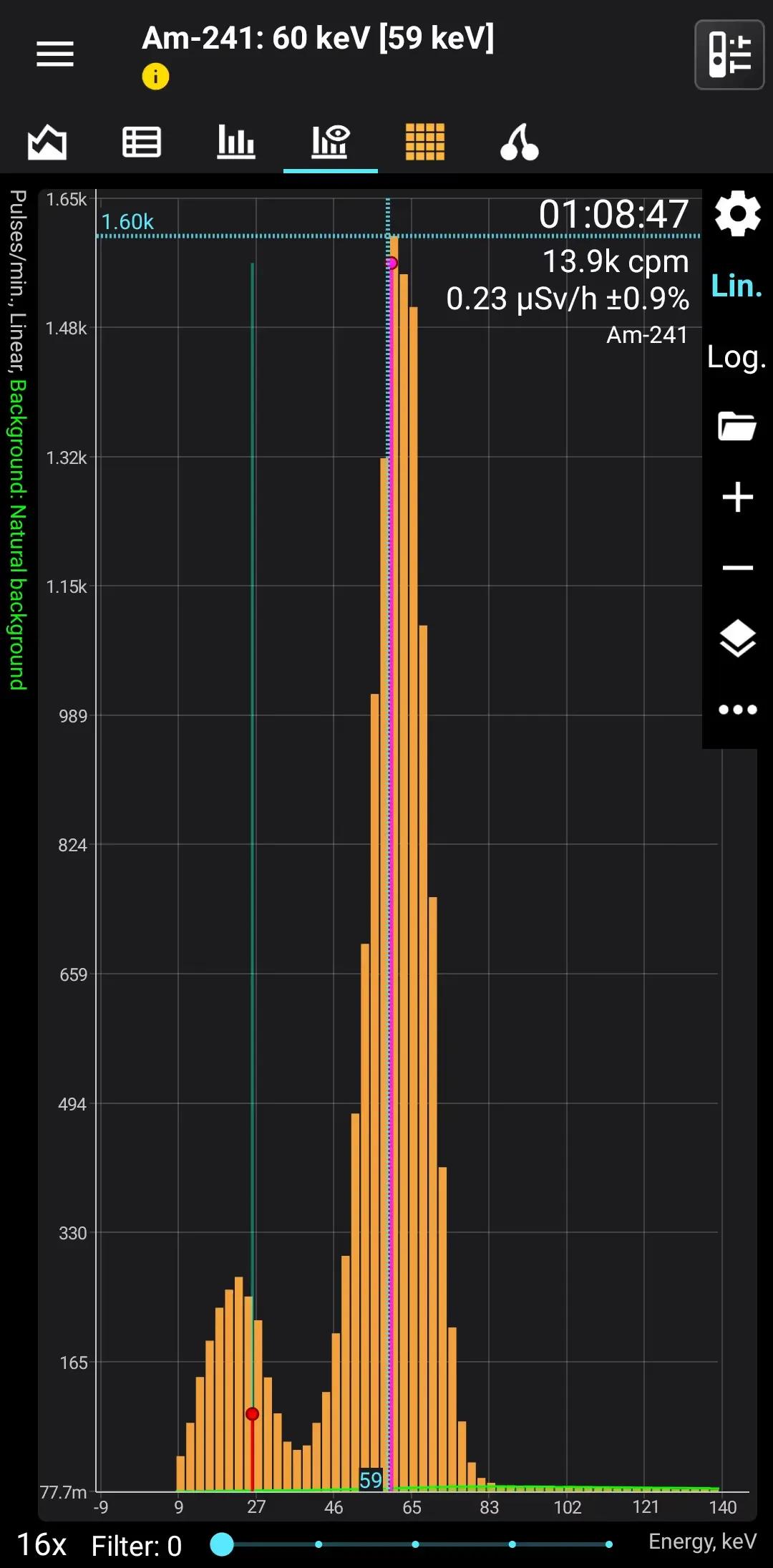
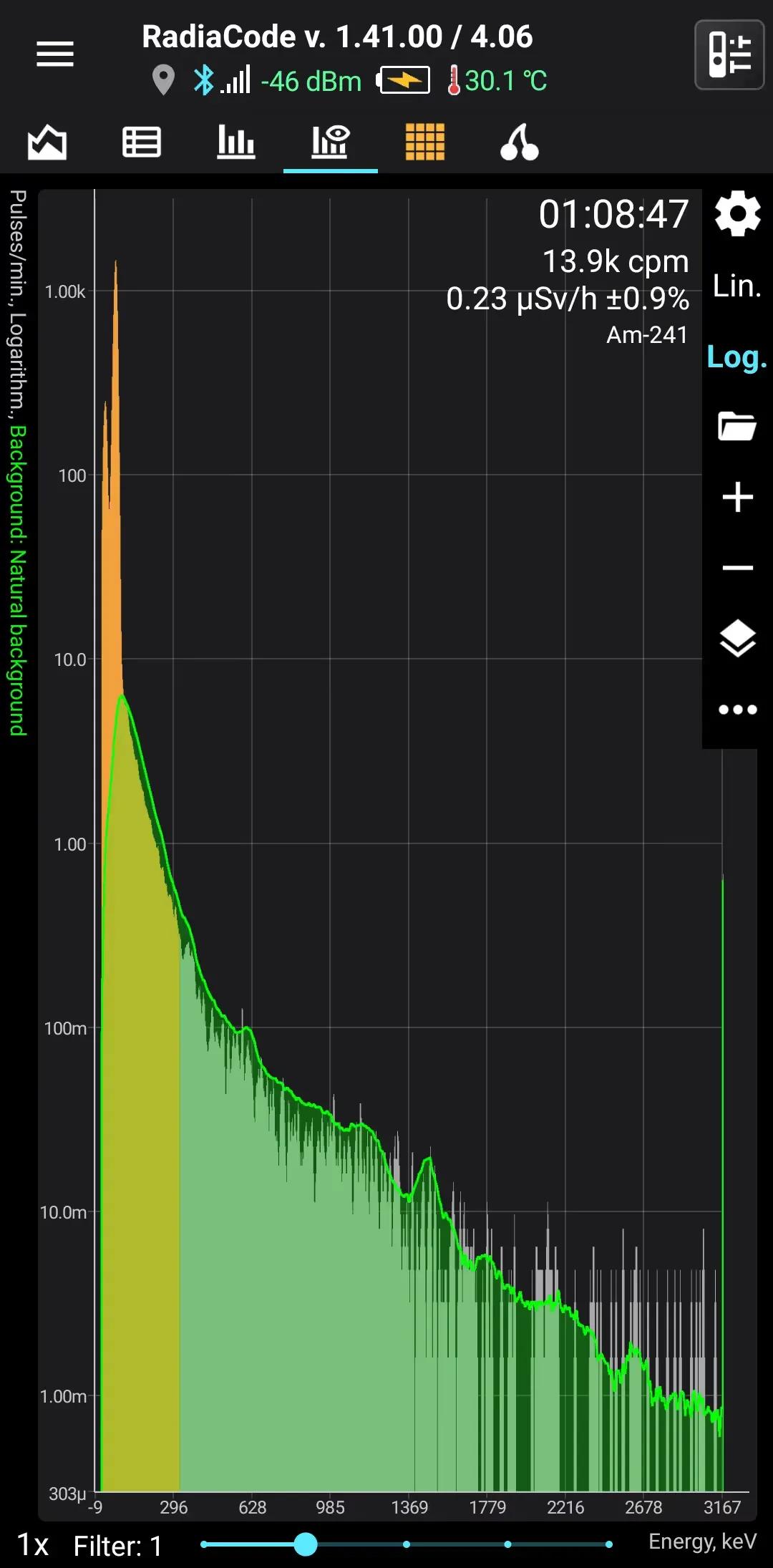
Am-241
Americium-241
Half-life: 432,6 years Main emission lines: 26, 59 keV
Decay mode Alpha
Alpha
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 5485.56 | 84.8 |
| 5442.80 | 13.1 |
| 5388 | 1.66 |
Gamma
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 59.5409 | 35.9 |
| 26.3446 | 2.27 |
X-rays
| Energy, keV | Intensity, % |
| 11.870 - 22.402 | 37 |